Gingivitis can occur when adequate attention is not paid to oral and dental care. In addition, malnutrition and some diseases can also trigger this condition.
This condition, which can also be called gingivitis, negatively affects people's quality of life. It also causes pain during eating and speaking.
What is Gum Inflammation?
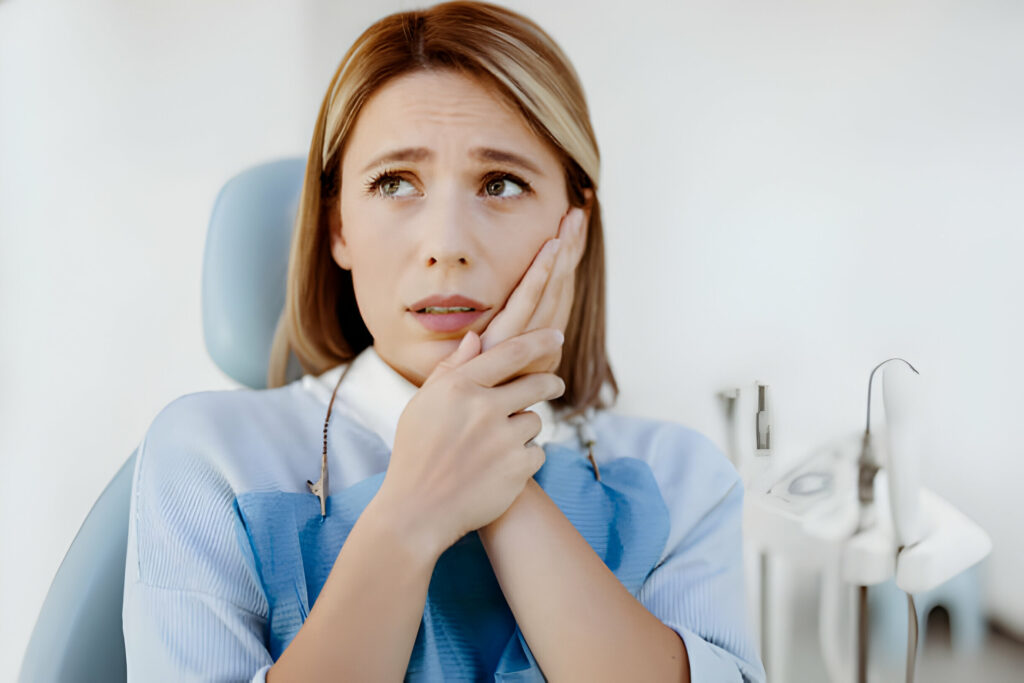

Poor oral hygiene and lack of attention to dental care can lead to gum inflammation. In addition, inadequate nutrition and certain illnesses can also trigger this condition.
Also known as gingivitis, this condition negatively affects individuals' quality of life and can cause discomfort during eating and speaking.
Causes of Gum Inflammation:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Regular dental visits are crucial as gum inflammation may occur without any noticeable symptoms. Inflammation in your gums can progress unnoticed and lead to various problems, including tooth loss.
Persistent Gum Inflammation:
What Causes Persistent Gum Inflammation?
Gums are not completely attached to the teeth; they form pocket-like structures by attaching from the distant part of the teeth. Over time, food debris can accumulate in these pocket-like areas.
When regular dental care is not practiced, leftover food particles can lead to the formation of plaques over time. Plaques are thin layers that can harden over time.
When plaques harden, they turn into tartar. Tartar buildup on the gums can cause inflammation. Over time, tartar buildup can cause the gums to detach from the teeth, leading to gum recession.
Risk Factors for Gum Inflammation:
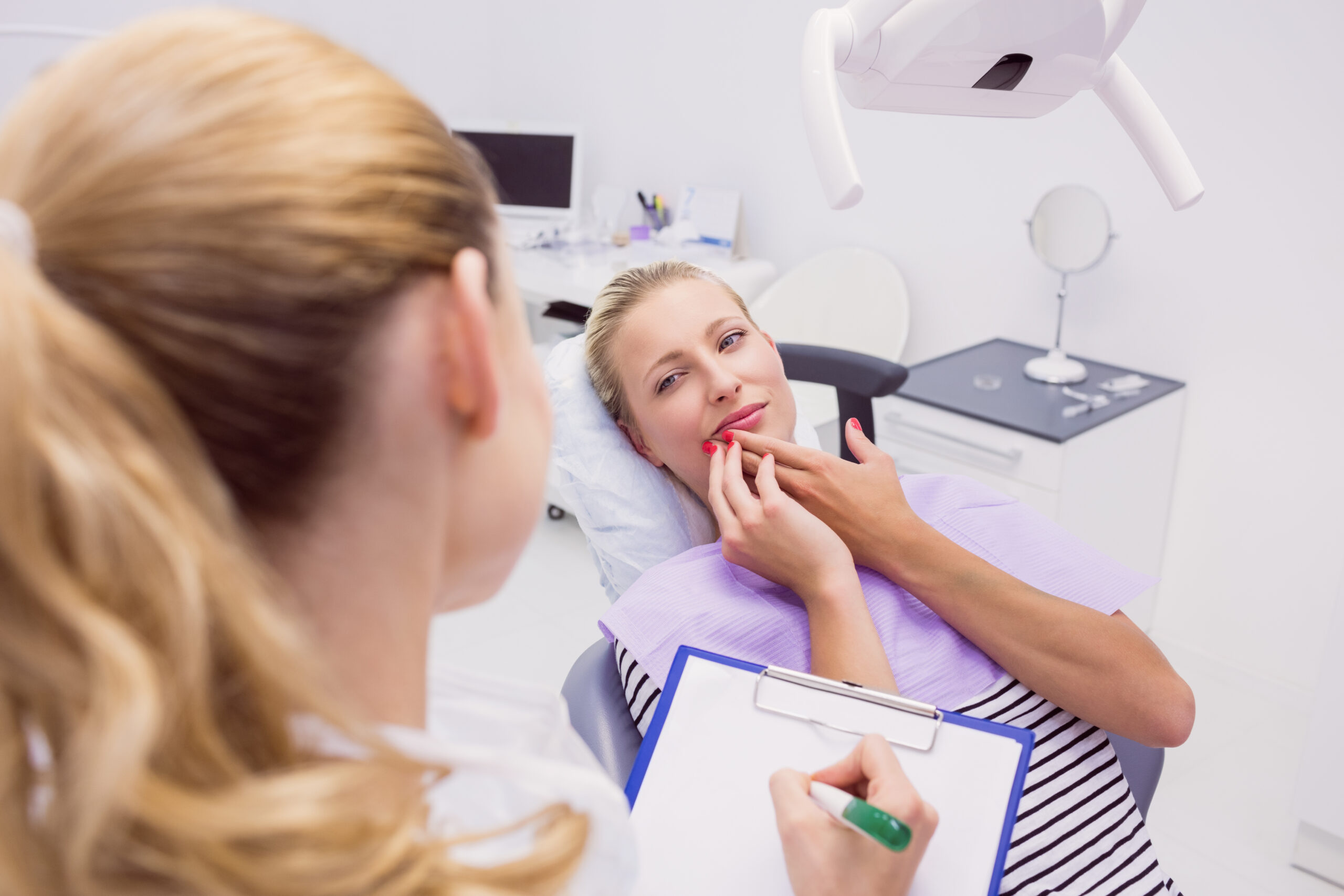

- Smoking and tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Certain medications
- Incorrect dental treatments
- Structural issues in teeth
- Genetics
- Poor oral hygiene
- Imbalanced nutrition
- Dentures
- Hormonal changes in women such as menstruation, pregnancy, menopause
- Aging
- Stress
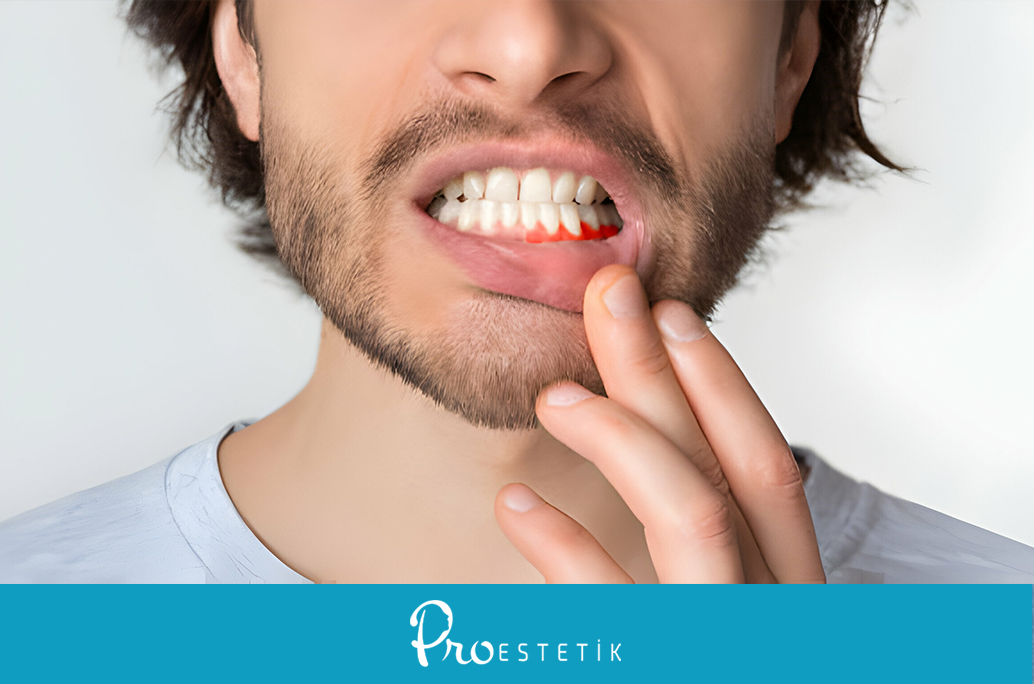
Signs of Gum Inflammation:
- Excessive sensitivity and swelling in the gums
- White-colored inflammations on the gums
- Bleeding during brushing
- Gum recession
- Pain during speaking and chewing
- Bad breath
- Sensitivity to hot and cold
- Loosening of teeth
- Darkening of gum color
Preventing Gum Inflammation:
- Brushing teeth properly at least twice a day
- Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing motions
- Not neglecting dental flossing and using it correctly
- Using mouthwash
- Adopting regular eating habits
- Regular dental check-ups
- Changing toothbrushes every three months
Can Gum Inflammation be Treated with Medication?
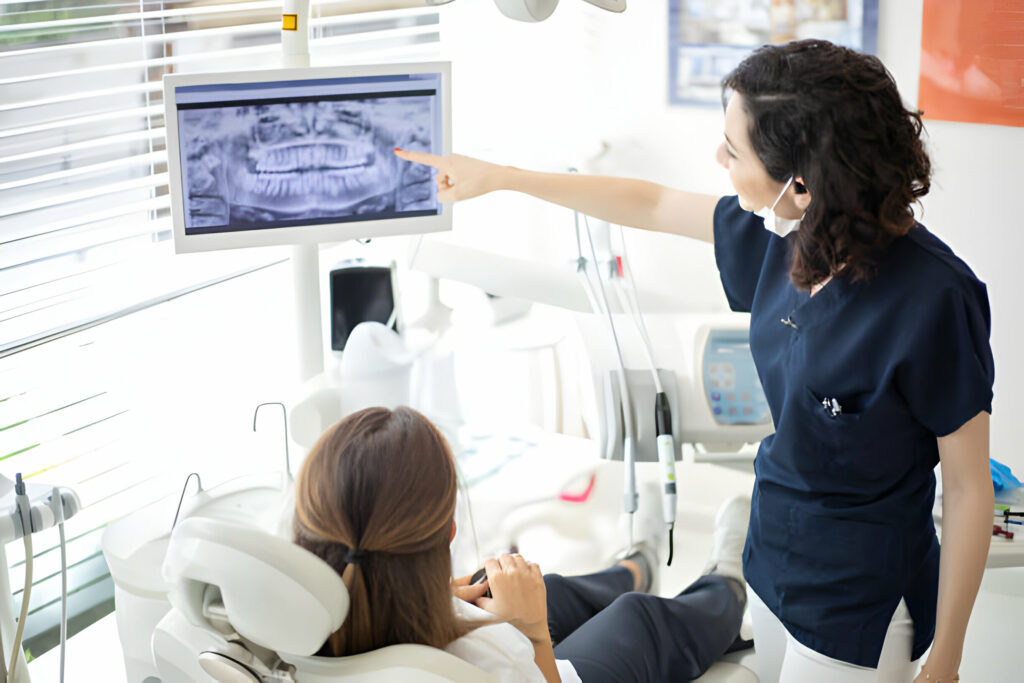

Gum inflammation can be treated with medication. However, it is essential to consult a dentist first. Antibiotics may be prescribed for a week in cases like gum inflammation. After completing the prescribed antibiotics, a follow-up appointment is necessary.
Can Inflammation Occur After Gum Surgery?
Inflammation after gum surgery is common as the gums are extra sensitive post-surgery. To prevent this, it is essential to follow the dentist's post-operative instructions and pay extra attention to oral hygiene.
Consequences of Untreated or Delayed Treatment of Gum Inflammation:
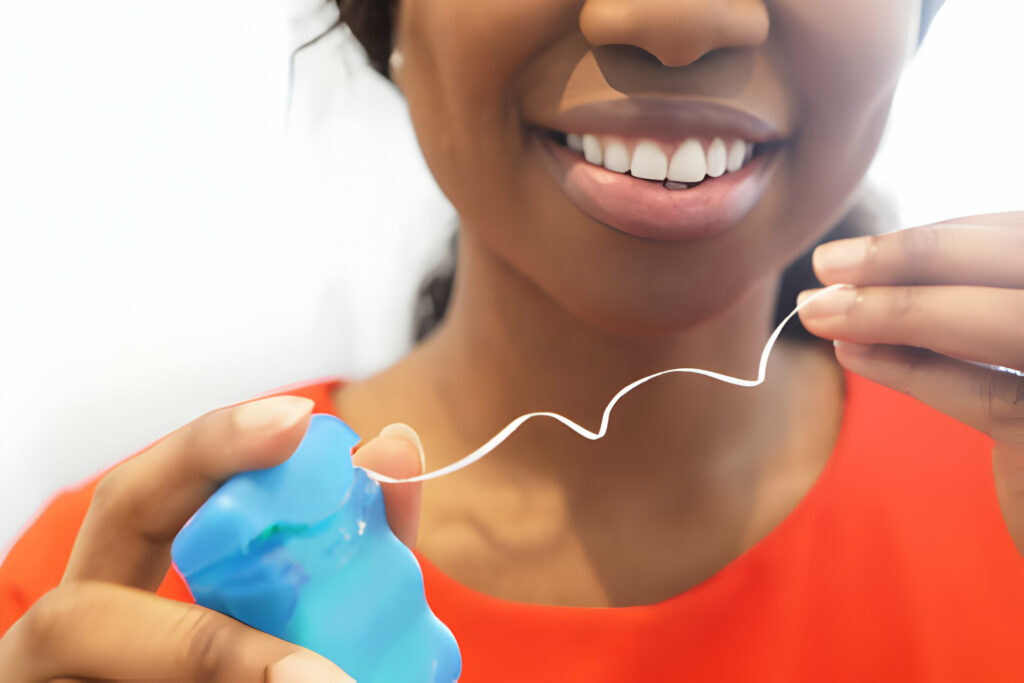

Untreated gum inflammation can lead to gum recession over time, affecting the connection between teeth and the mouth. This can cause damage to the tissues supporting the teeth, leading to periodontitis, a severe infection that can even result in tooth loss.
Why Are Gums More Sensitive During Menstruation, Pregnancy, and Menopause?
Hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause affect the entire body, including the gums. As a result, hormonal fluctuations can impact gum sensitivity, leading to bleeding and discomfort.
Gum inflammation is a serious issue with various symptoms. Promptly seeking help from a dentist is crucial for addressing this problem effectively. Ignoring dental issues can have negative effects on oral and dental health. Early diagnosis and swift treatment are vital in managing dental problems effectively. You can visit our clinic for prompt diagnosis, rapid, and accurate treatment services, and take advantage of our free initial consultation offer.

 English
English Turkish
Turkish Deutsch
Deutsch العربية
العربية![[:en]What is Gum Inflammation? | 9 Signs of Gum Inflammation![:tr]Diş Eti İltihabı Nedir?| Diş Eti İltihabı 9 Belirtisi![:de]Was ist Zahnfleischentzündung? | 9 Anzeichen für Zahnfleischentzündung![:ar]ما هو التهاب اللثة؟ | 9 علامات لالتهاب اللثة![:] dis-eti-iltihabi](https://proestetik.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/dis-eti-iltihabi7.png)