The teeth are firmly attached to the jawbone and are thought to be straight and fixed unless they are hit hard. Therefore, outside of orthodontic treatments, teeth do not appear to move. However, teeth shifting is a common occurrence outside of braces and aligners. Unless this problem is left untreated, it causes not only jaw closure but also various problems such as facial, jaw and neck pain.
You should consult your dentist when any difference in tooth alignment is observed. After determining why the teeth are shifted, the most appropriate treatment method is decided by the dentist and the treatment is started.
Tooth Displacement
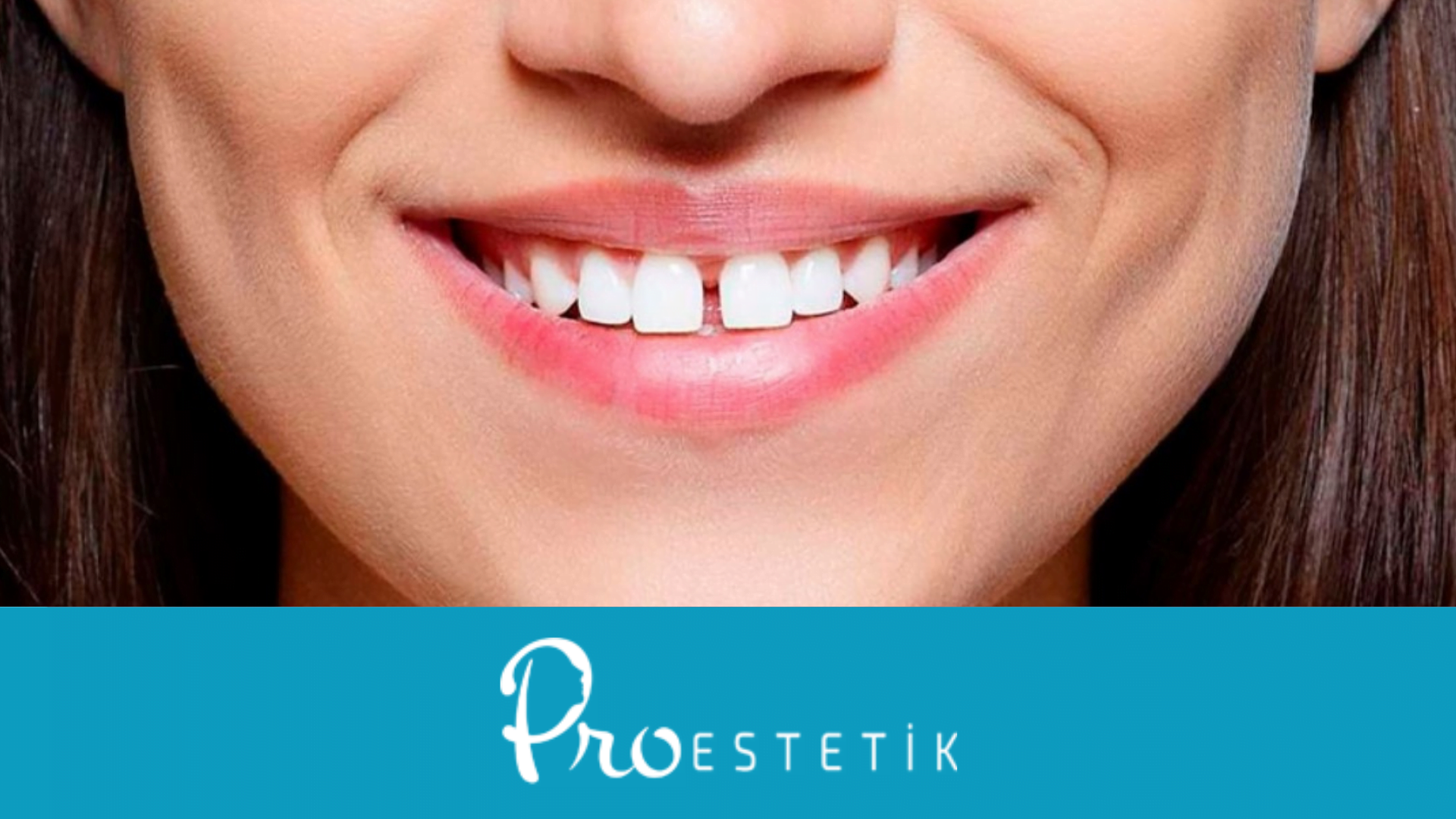
Tooth displacement refers to the condition where teeth shift from their normal position. This often occurs when teeth move away from their correct places on the jawbone. Tooth displacement can result from various factors such as inadequate space in the mouth or congenital abnormalities in jaw structure.
Causes of Tooth Displacement

Several factors can contribute to tooth displacement:
- Inadequate Space: Insufficient space within the mouth can lead to teeth becoming crowded or misaligned over time.
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): Individuals may grind their teeth, especially during sleep due to factors like anxiety or stress. The pressure exerted on the teeth over time can cause them to shift.
- Tooth Loss: When a tooth is lost, the surrounding teeth may move to fill the gap, resulting in displacement. Failure to address this can lead to significant jaw issues.
- Congenital Factors: Genetic factors such as jaw structure or the shape and size of teeth can increase the risk of tooth displacement.
- Gum Diseases: Gum diseases can damage the gum tissues over time, leading to inadequate support for the teeth and subsequent displacement.
- Trauma: A blow to the jaw area can damage the jawbone and cause teeth to shift.
Treatment of Tooth Displacement
Various treatment methods are available to address tooth displacement, depending on the severity, cause, and individual needs:
- Orthodontic Treatment: Braces or dental aligners are commonly used to correct tooth misalignment. Brackets and wires applied to the teeth gradually move them back into position over time, allowing for proper jaw function and bite alignment.
- Tooth Extraction: In some cases, tooth extraction may be necessary to create space for crowded or impacted teeth.
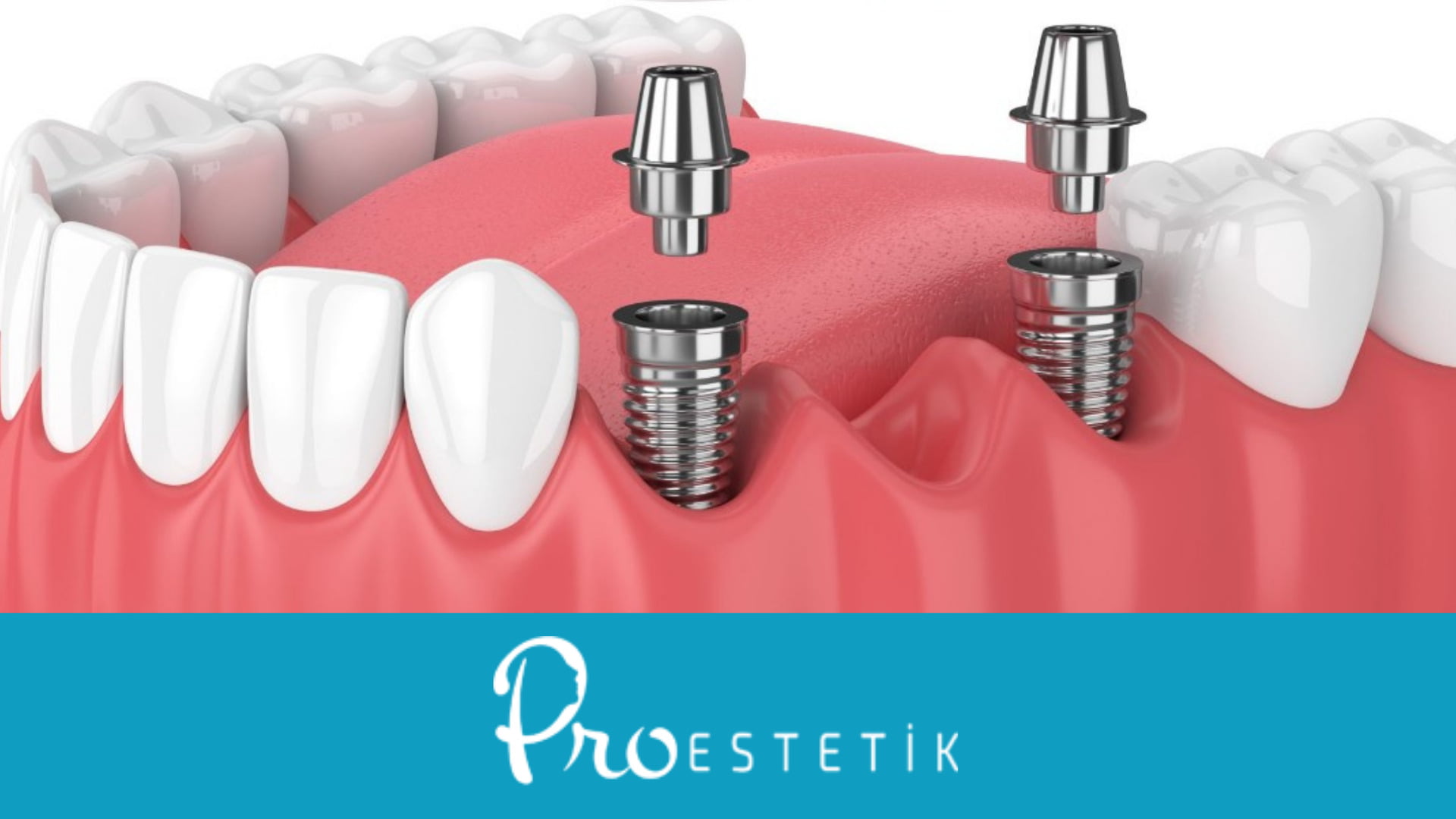
- Dental Implants: Implants can be used to replace missing teeth, preventing future displacement and restoring proper alignment.
- Other Orthodontic Devices: Depending on the specific case, other orthodontic appliances or devices may be used to address tooth displacement.
Prevention of Tooth Displacement
While it may not always be possible to completely prevent tooth displacement, several measures can help mitigate the risk:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Routine dental visits can help identify potential issues, including tooth displacement, early on, allowing for appropriate treatment.
- Good Oral Hygiene: Daily brushing and flossing can prevent tooth decay and gum diseases, reducing the risk of tooth displacement.
- Managing Bruxism: Seeking treatment for teeth grinding can prevent future displacement caused by excessive pressure on the teeth.
- Protective Measures: Taking precautions to prevent trauma to the jaw area, especially during sports or physical activities, can help reduce the risk of tooth displacement.
By addressing tooth displacement early and following preventive measures, individuals can maintain optimal oral health and prevent associated complications.

 English
English Turkish
Turkish Deutsch
Deutsch العربية
العربية![[:en]What is Tooth Displacement? Why Does it Occur? How is it Treated?[:tr]Diş Kayması Nedir? Neden Olur? Nasıl Tedavi Edilir?[:de]Was ist Zahnverschiebung? Warum tritt es auf? Wie wird es behandelt?[:ar]ما هي تحركات الأسنان؟ لماذا تحدث؟ وكيف يتم علاجها؟[:] diş kayması](https://proestetik.com.tr/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/dis-kaymasi.jpg)